The history of programmatic advertising is very much a contribution of several entities. It evolved gradually, come the turn of the millennium. But, during the early 2000s, Double-click (now under Google) was one of the first to implement it. The company introduced tools to automate the process of serving ads to websites. A revolution in paid marketing. But a few beginners might have one question that what is programmatic advertising? So, let’s learn about it.
What is Programmatic Advertising?
Programmatic advertising is the automated process of buying and selling ad spaces. Publishers with available inventory can sell it to advertisers who want to promote their business/service via ads.
It is essentially the same as any other display ad on a website. The main differentiator is programmatic media buying. It allows you to bid on ad spaces and run them in real time. There are several different types of media buying: Real-time bidding, private marketplace, programmatic guaranteed, and preferred deals. Each of these has slightly different ways to buy and sell ads.
How Does Programmatic Advertising Work?
The process of programmatic advertising starts uses 7 components. First, let’s learn about them.
The 7 Components of Programmatic Advertising
1. Ad Creative – The ad creative is the basic element of any ad. It is the actual visual or interactive content in the form of images, GIFs, Text, or video being displayed to the target audience. All ads need a creative to attract the visitor and compel them to take the desired action.
2. Ad Inventory – Ad Inventory is available ad space on websites, mobile apps, and other digital platforms where ads can be displayed. Advertisers buy ad spaces from the available inventory to display their creatives/ads.
3. Demand-Side Platform (DSP) –Advertisers and agencies use DSPs to manage and optimize their programmatic ad campaigns. It has tools that allow you to set campaign parameters, select targeting criteria, and manage budgets. It is also the platform that advertisers use to bid on available ad spaces.
4. Supply-Side Platform (SSP) – Publishers and websites use an SSP to manage their digital ad inventory. It is the DSP equivalent for publishers (suppliers). It allows them to connect with multiple ad exchanges and advertisers to auction their ad spaces.
If you are looking to implement B2B advertising services in your business, learn how B2B advertising services can help you!

5. Ad Exchange –An ad exchange is a marketplace that connects DSPs from advertisers to SSPs of publishers. This is where all the buying and selling of ad inventory happens with real-time bidding. Advertisers bid for impressions, and publishers offer their ad space, all of which happens in milliseconds.
6. Data Management Platform (DMP) –Advertisers use DMP to collect, organize, and analyze audience data. You can use this tool to create detailed audience segments based on various attributes. This allows you to target specific segments of your target audience and serve relevant ads.
7. Ad Server –An ad server is responsible for delivering ads to websites and apps. It handles the scheduling, targeting, and tracking of ads. This way, the ads reach the intended users correctly.
The Process Flow for Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising involves several interconnected steps that allow advertisers to automate the buying, selling, and delivery of digital ads. Here’s an overview of the core process:
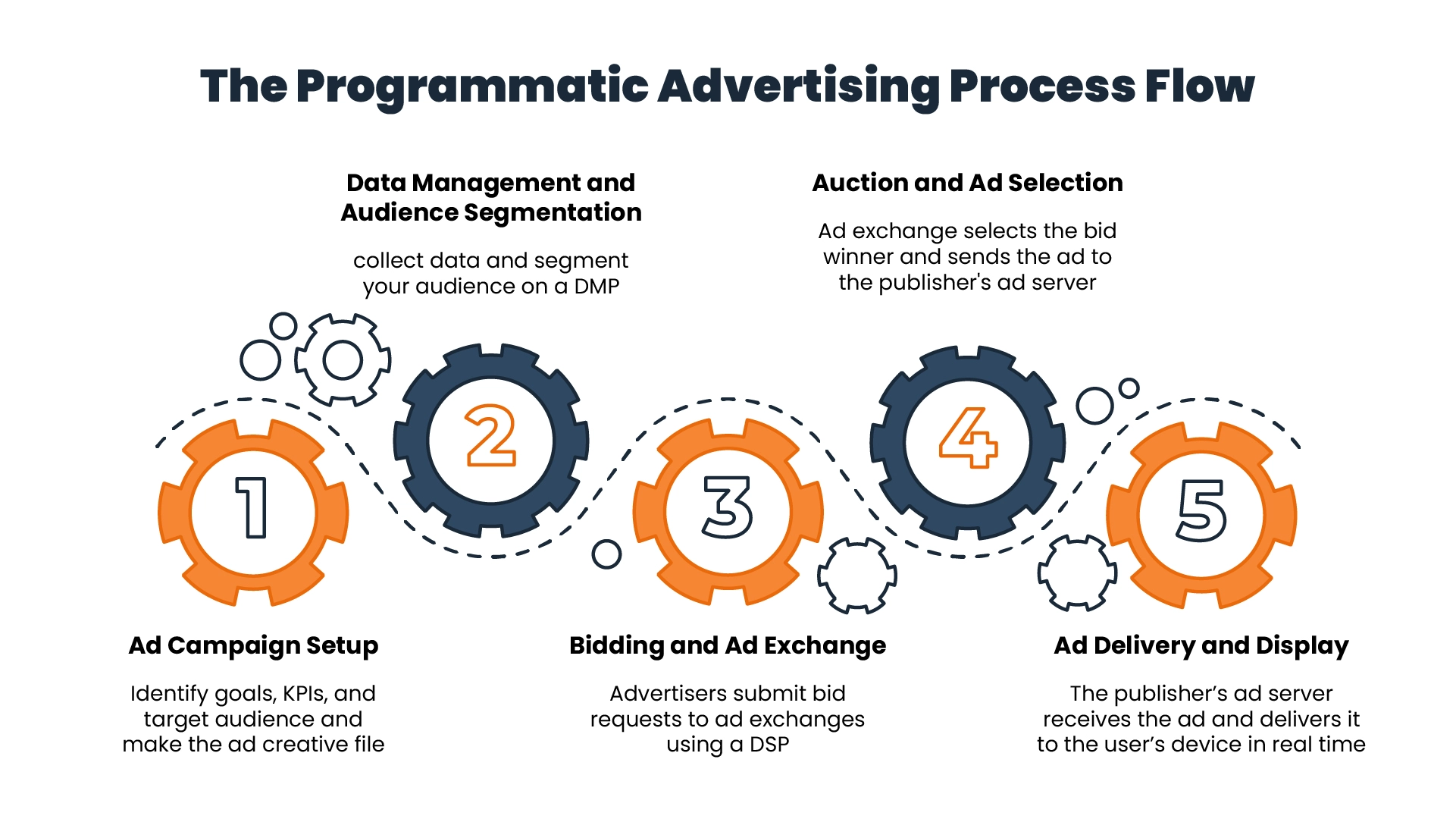
1. Ad Campaign Setup
Rather than the first step, this is more like step 0 of programmatic advertising. For the campaign setup, advertisers set their budget, target audience, goals, and KPIs. Then they create an ad creative specific to these parameters.
2. Data Management and Audience Segmentation
In this step, advertisers use a DMP to collect, organize, and segment audience data. This allows them to create cohorts based on factors like demographics, behavior, interests, and past integrations.
3. Bidding and Ad Exchange
This is the step where programmatic media buying begins. Advertisers use a DSP to submit bid requests to ad exchanges for available ad impressions. The ad exchange holds real-time auctions where multiple advertisers bid for the same impressions. Then, the DSP algorithms analyze available data to bid accordingly.
4. Auction and Ad Selection
Once the ad exchange selects the bid winner with the highest price or other factors, the ad is chosen and sent to the publisher’s ad server.
5. Ad Delivery and Display
Once the publisher’s ad server receives the ad, it delivers that ad to the user’s device in real time as per the criteria. This is where the core process ends. Next are a few additional steps that bring programmatic advertising to a full circle.
After the user sees the ad and interacts with it, you move on to tracking and measuring the success of the ad. After an informative report, you can move to optimize the ad, adjust the budget, and repeat the process all over again for micro-improvements.
Final Words
Programmatic Advertising is a process that many marketers have a lot of confusion about. I hope this article cleared it up a little. Now, you can identify how it works to start thinking about a strategy for your business.
If you want to learn about real-time case studies and future trends in programmatic advertising, do not forget to check out UnboundB2B’s programmatic advertising ebook for free.

Our blog
Latest blog posts
Tool and strategies modern teams need to help their companies grow.

In the absence of a solid lead scoring system, your sales team will spend time pursui...

Programmatic ABM combines the effectiveness of targeted engagement with automation. I...

Take advantage of the year-end holiday rush so you can boost your SaaS revenue and st...





